
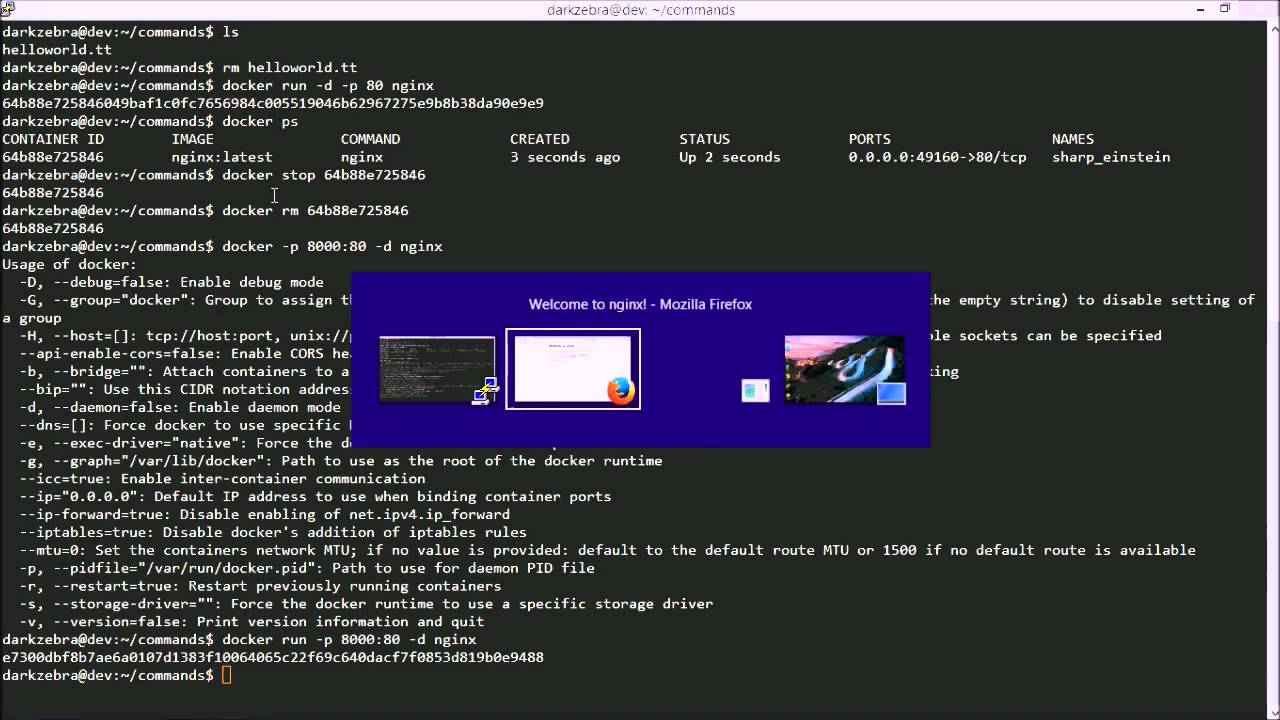
This example runs an interactive bash shell p HOST:CONTAINERĪttach to `STDIN`, `STDOUT` and/or `STDERR`.įor interactive processes (like a shell), you must use -i -t together in order to allocate a ttyĪssign a network to running container i.e.4.2.1 Configuring How Docker Restarts Containers 4.2.2 Controlling Capabilities and Making Host Devices Available to Containers 4.2.3 Accessing the Host's Process ID Namespace 4.2.4 Mounting a Host's root File System in Read-Only ModeĪpplication inside a container, for ~]# docker run -i -t -name guest oraclelinux:6.8 ~]# cat /etc/oracle-release
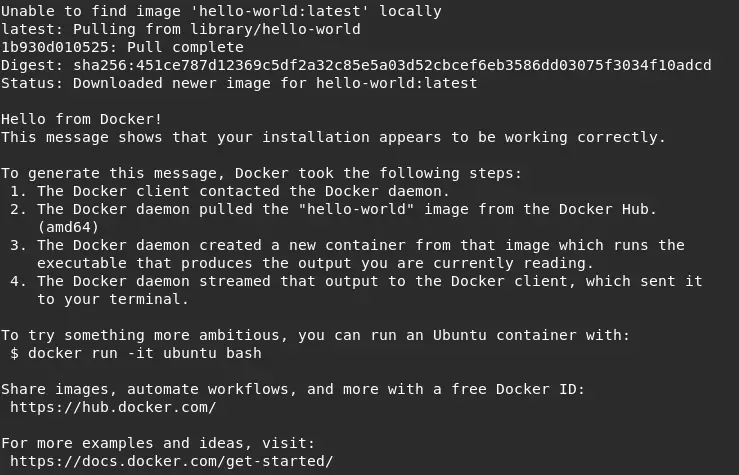
Makes container port to be available on specific host port i.e. Run container in the background, print new container id Let's have a look at what popular available options that we can use for this specific command: While these commands are not available in hello-world image file systemĭocker image contains following two things:ĭifferent docker images can contain different file systems depending upon how these images are build. Ls and echo commands are available in busybox image file system The reason why these commands does not work inside hello-world image is because Let's have a look at the output of the above command:

Let's verify this by running same commands with different docker image called hello-world: So basically, your image can decide what resources that is required for this image containers. If you remember my last tutorial on docker image and container you know that each container reserves specific resources discribed by image that is used to create this container. The image we choose to run a container contains some commands of linux system and that is why we are able to run this command in this specific container. Note: You wont be able to run default command in all containers # Display list of files when container runs # Display Hello There text when container runs Open your terminal window again and let's run following command: Let's understand above diagram practically. Let's have a look at following new diagram: Once image is downloaded it created and ran the containerĭocker run command can also override a default command that container runs when it is created. It found the image on docker hub and then downloaded it and stored in cache It did not find this image locally and then talked to docker hub It does following when we ran above command:
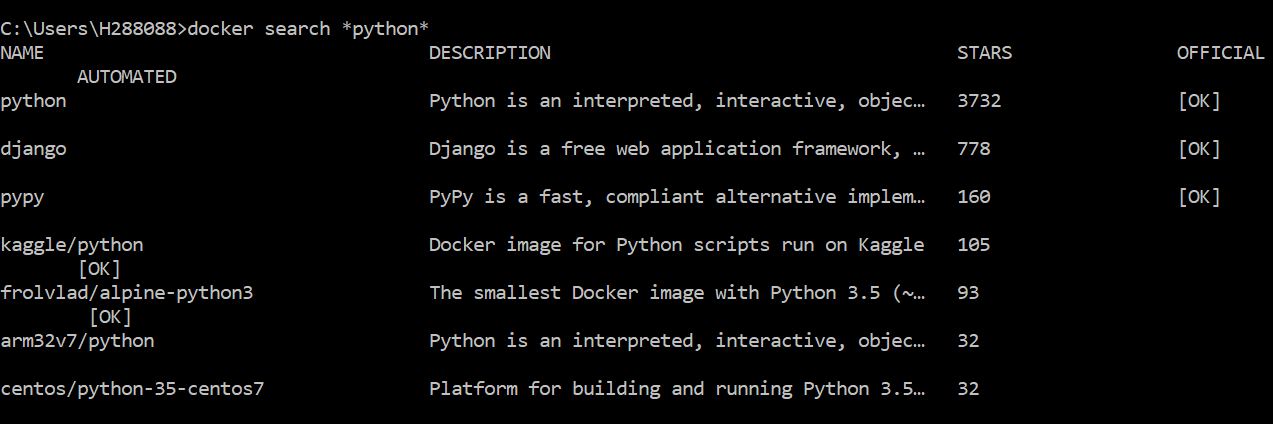
Let's take an example, open your terminal window and try running following command: If image can not be found on local or on docker hub it gives you no error and does nothing If it finds the image it downloads it store in the image cacheĬreates a container from the downloaded or local image If image is not found it tries to find image on Docker hub If you do not have an image it does following things: You need to have an image first in order to run this command. Run a newly created or previously created container from the image provided Let's have a look at the diagram to understand more about this command:ĭocker run command is used to do following things:Ĭreate a new container if it does not exist I would suggest you read below article to learn about docker image and container before you start reading this tutorial: In this tutorial we will learn in depth about docker run command.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
